What Is a Tumor
A tumor is an abnormal growth of cells in the body.
Our body cells normally grow, divide, and die in a controlled way. When this process goes wrong, cells may grow excessively and form a lump or mass. This mass is called a tumor.
Tumors can develop almost anywhere in the body, including the brain, breast, skin, lungs, and uterus.
Types of Tumors
Tumors are generally classified into three main types:
1. Benign Tumors
Benign tumors are not cancer.
They:
• Grow slowly
• Do not spread to other parts of the body
• Usually have clear boundaries
• Often can be removed completely
In many cases, benign tumors are not life threatening. However, they can still cause problems if they press on nearby organs or nerves.
Examples include:
• Fibroids in the uterus
• Lipomas under the skin
• Certain types of brain tumors
2. Malignant Tumors
Malignant tumors are cancerous.
They:
• Grow rapidly
• Invade nearby tissues
• Can spread to other parts of the body through blood or lymph system
• May return even after treatment
This spreading process is called metastasis, and it is what makes cancer dangerous.
3. Premalignant Tumors
Some tumors are not cancer yet but have the potential to become cancer in the future. These are called premalignant or precancerous growths.
Doctors often monitor or remove them early to prevent progression.
What Makes a Tumor Cancerous
A tumor becomes cancerous when its cells:
• Grow uncontrollably
• Invade surrounding tissues
• Spread to distant organs
• Avoid normal cell death
Cancer cells behave differently from normal cells. They ignore the body’s control systems and continue multiplying.
How Do Doctors Know If a Tumor Is Cancerous
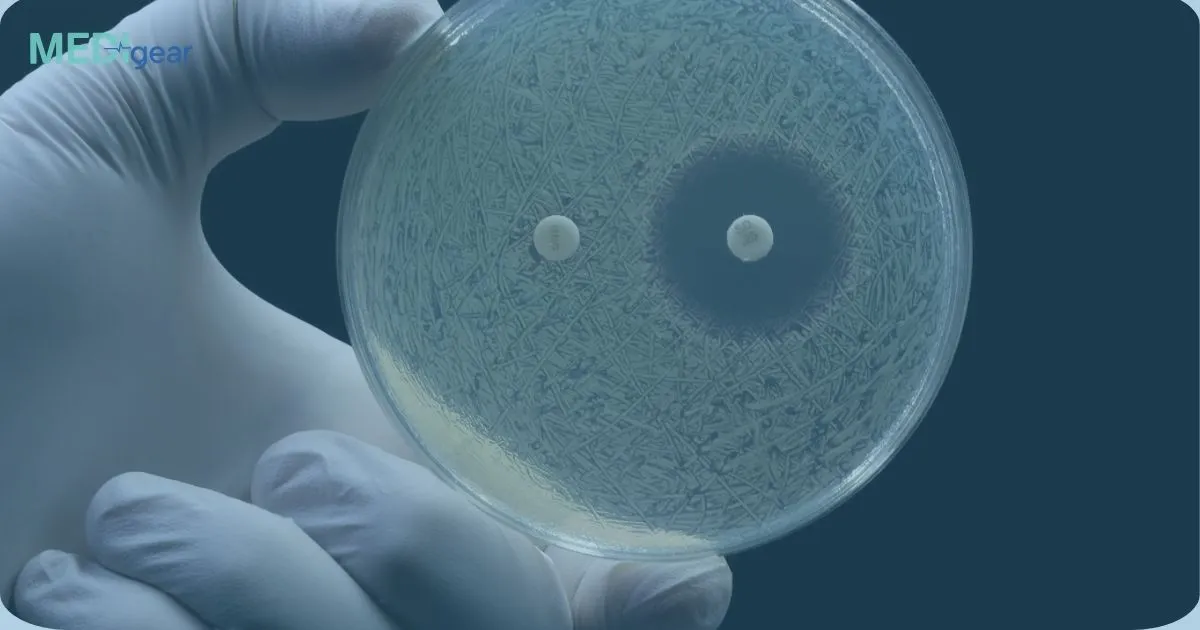
The only way to confirm whether a tumor is cancerous is through medical testing.
Common methods include:
• Imaging tests such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI
• Biopsy, where a small sample of tissue is examined under a microscope
• Blood tests in certain cases
A biopsy is the most reliable method to determine whether a tumor is benign or malignant.
Can Benign Tumors Turn Into Cancer
Most benign tumors do not turn into cancer.
However, some types of benign growths can become cancerous over time. That is why doctors may recommend monitoring or removing certain tumors even if they are not cancer at the time of diagnosis.
Regular medical follow up is important.
Symptoms of Tumors
Symptoms depend on the tumor’s size and location.
Some tumors cause no symptoms and are discovered accidentally during routine tests.
Possible signs may include:
• A visible lump
• Persistent pain
• Unexplained weight loss
• Fatigue
• Changes in bowel or bladder habits
• Unusual bleeding
These symptoms do not always mean cancer, but they should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
Are All Lumps Cancer
No. Many lumps are harmless.
Common noncancerous causes include:
• Cysts
• Swollen lymph nodes
• Fat deposits
• Infections
It is always best to consult a doctor if you notice a new lump that does not go away.
Treatment Differences
Treatment depends on whether the tumor is benign or malignant.
Benign tumor treatment may include:
• Monitoring
• Surgical removal if necessary
Cancer treatment may involve:
• Surgery
• Chemotherapy
• Radiation therapy
• Targeted therapy
• Immunotherapy
Early diagnosis greatly improves outcomes for cancer.
The Bottom Line
Not all tumors are cancerous.
A tumor is simply an abnormal growth of cells. Some are harmless and slow growing, while others are cancerous and can spread.
If you notice unusual symptoms or a new lump, seek medical advice. Early evaluation provides clarity and peace of mind.
Understanding the difference between benign and malignant tumors can help reduce fear and encourage timely medical care.